Reminder: Please stop the video before closing this pop-up.
The problem
Atrial fibrillation (AF) is the most common type of arrhythmia, predicted to affect 6–12 million people in the USA by 2050 and 17.9 million in Europe by 2060 (Ref). The gold standard treatment of AF – catheter ablation – is far from perfect, with recurrence of AF a very common phenomenon (Ref). There is a high unmet need for developing better medical treatment of this common condition.
Key clinical finding
A single injection of botulinum toxin into epicardial fat pads in patients undergoing cardiac surgery resulted in long term (3 years +) substantial reduction in incidence of postoperative AF, a condition that affects up to 50% of all patients (Ref)
Why Novochizol?
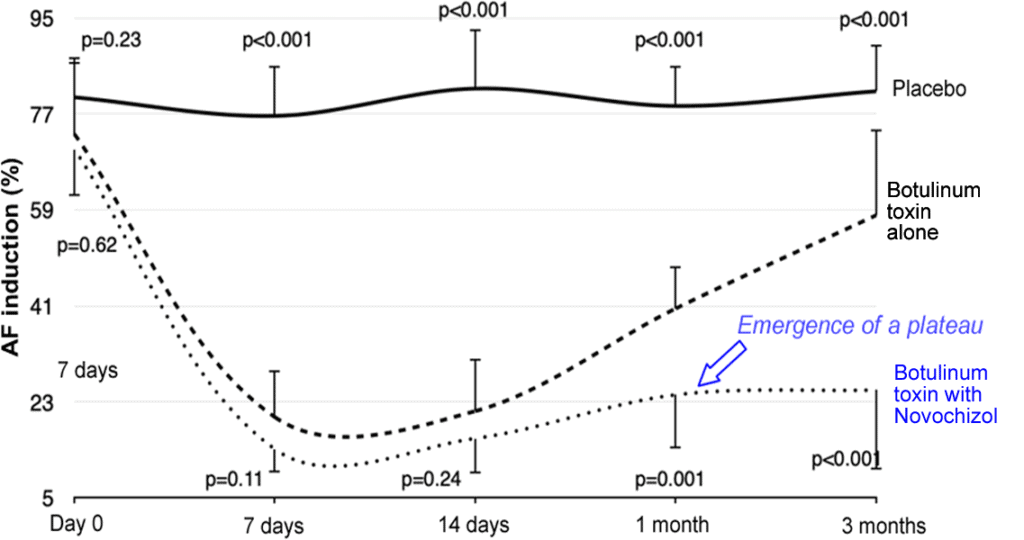
– Injections of NovochizolTM-botulinum toxin formulations into canine epicardial fat pads resulted in extended complete abolition of cardiac vagal responses and increased suppression of atrial fibrillation (Ref).
– NovochizolTM formulations of botulinum toxin result in a 40% increase of LD50 which significantly extends the therapeutic range of the drug in the clinical setting, offering a safe higher dose to patients that do not respond to lower doses. This advantage may be explained by the absence of systemic distribution of NovochizolTM formulations, confirmed in multiple studies (Ref).
Reminder: Please stop the video before closing this pop-up.
Reminder: Please stop the video before closing this pop-up.
Reminder: Please stop the video before closing this pop-up.
Reminder: Please stop the video before closing this pop-up.